Table of Contents
Windows でフォルダを開き、そこに表示されるあるフォルダを別のフォルダにドラッグアンドドロップすると、ファイルの移動が行われます。 フォルダごとコピーして別の場所に貼り付ければフォルダのコピーが行われます。 しかし、ファイルコピーにかかる時間を計算するため、ファイルコピー開始までに時間がかかったり、ファイルのコピー作業が一向に終わらないことがあります。
ここでは、その遅いファイルのコピーを早く終わらせるための方法を紹介します。
方法
XCOPYコマンドを使います。
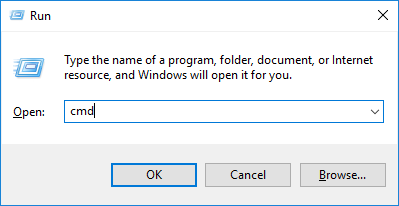
まず、 Windows Key + R を押して出てきたウインドウで cmd と入力して Enter を押します。
コマンドプロンプトが起動しますのでそこで XCOPYコマンドを使用します。 XCOPYコマンドは次のようにして使用します。 重要なオプションをリストアップしました。
XCOPY
基本は XCOPY source_dir destination という使い方です。 サブディレクトリも含めてコピーするには下のオプションを使います。
オプション
- /S
- 空のディレクトリを除いて、サブディレクトリも含めてコピーします。
- /E
- 空のディレクトリも含めて、サブディレクトリを含めてコピーします。
- /Q
- コピー中の画面表示をなしにします。 表示処理がなくなるのでそれだけ高速になります。
使用例
- サブディレクトリを含めてコピーする場合
-
1XCOPY C:\FROM C:\TO /S
- 空のサブディレクトリも含めてコピーする場合
-
1XCOPY C:\FROM C:\TO /E
- 画面表示もオフにして、サブディレクトリを含めてコピーする場合
-
1XCOPY C:\FROM C:\TO /E /Q
この XCOPY を使ってフォルダをコピーすると、通常のコピー・ペーストよりも高速にコピーができます。
XCOPY の詳しい説明
コマンドプロンプトで XCOPY /? を実行すると、 XCOPY の説明が下記のように表示されます。 上で紹介した以外にも、複数のオプションが用意されており、「ある日付以降に編集されたファイル」のみに絞ってコピーすることなども可能です。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 |
Copies files and directory trees. XCOPY source [destination] [/A | /M] [/D[:date]] [/P] [/S [/E]] [/V] [/W] [/C] [/I] [/Q] [/F] [/L] [/G] [/H] [/R] [/T] [/U] [/K] [/N] [/O] [/X] [/Y] [/-Y] [/Z] [/B] [/J] [/EXCLUDE:file1[+file2][+file3]...] source Specifies the file(s) to copy. destination Specifies the location and/or name of new files. /A Copies only files with the archive attribute set, doesn't change the attribute. /M Copies only files with the archive attribute set, turns off the archive attribute. /D:m-d-y Copies files changed on or after the specified date. If no date is given, copies only those files whose source time is newer than the destination time. /EXCLUDE:file1[+file2][+file3]... Specifies a list of files containing strings. Each string should be in a separate line in the files. When any of the strings match any part of the absolute path of the file to be copied, that file will be excluded from being copied. For example, specifying a string like \obj\ or .obj will exclude all files underneath the directory obj or all files with the .obj extension respectively. /P Prompts you before creating each destination file. /S Copies directories and subdirectories except empty ones. /E Copies directories and subdirectories, including empty ones. Same as /S /E. May be used to modify /T. /V Verifies the size of each new file. /W Prompts you to press a key before copying. /C Continues copying even if errors occur. /I If destination does not exist and copying more than one file, assumes that destination must be a directory. /Q Does not display file names while copying. /F Displays full source and destination file names while copying. /L Displays files that would be copied. /G Allows the copying of encrypted files to destination that does not support encryption. /H Copies hidden and system files also. /R Overwrites read-only files. /T Creates directory structure, but does not copy files. Does not include empty directories or subdirectories. /T /E includes empty directories and subdirectories. /U Copies only files that already exist in destination. /K Copies attributes. Normal Xcopy will reset read-only attributes. /N Copies using the generated short names. /O Copies file ownership and ACL information. /X Copies file audit settings (implies /O). /Y Suppresses prompting to confirm you want to overwrite an existing destination file. /-Y Causes prompting to confirm you want to overwrite an existing destination file. /Z Copies networked files in restartable mode. /B Copies the Symbolic Link itself versus the target of the link. /J Copies using unbuffered I/O. Recommended for very large files. The switch /Y may be preset in the COPYCMD environment variable. This may be overridden with /-Y on the command line. |